#
Device installation
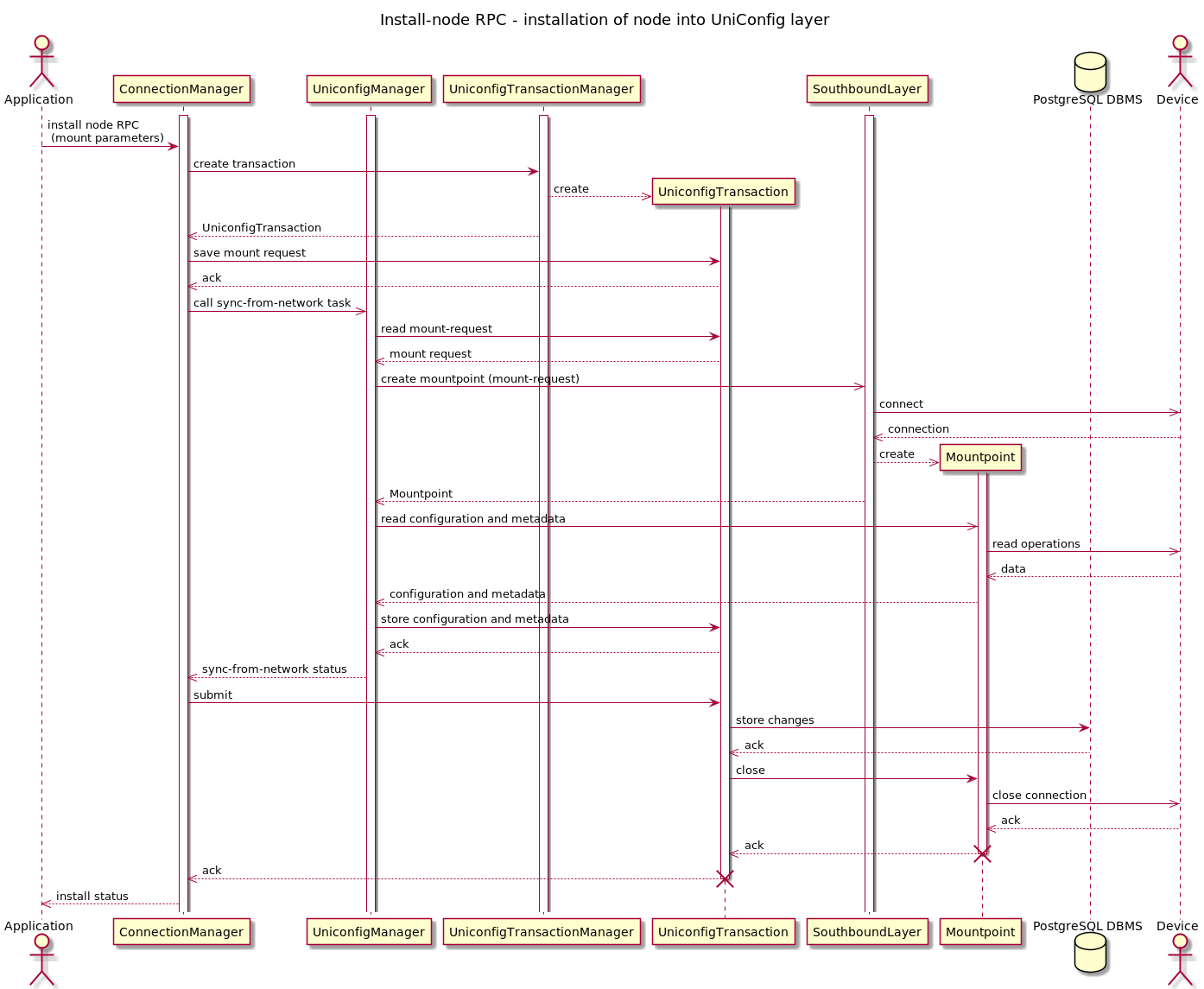
Installing is the process of loading device information into UniConfig database. This information is saved in PostgreSQL database and used whenever transaction occurs. When the transaction is finished the connection to device is closed again, until next transaction.
These are the steps of installation process:
- creation of UniConfig transaction
- creation of mountpoint - connection to device
- loading configuration and metadata from mountpoint
- closing mountpoint and connection to device
- storing synced configuration and metadata to database
- closing UniConfig transaction
Node can be installed only once (you will receive error if node has already been installed).
You can specify if you would like to install node on the UniConfig layer. Default value is 'true':
uniconfig-config:install-uniconfig-node-enabledOnly 1 node with the same node-id can be installed on UniConfig layer.
It is synchronous: it succeeds only after node is successfully installed it fails in other cases – max-connection-attempts is automatically set to value '1', if different value is not provided in RPC input, database or config file.
Following sections provide deeper explanation of parameters needed for installation, along with example install requests.
Overview of our OpenAPI along with all parameters and expected returns can be found here.
#
Default parameters
All install parameters (CLI/NETCONF) are set in database when Uniconfig is initializing. Values of these parameters are equal to specific yang model default values. These parameters are used when they are missing in RPC request.
Priority of using install parameters :
- Parameter set in install RPC request
- Parameter set in database
- Default parameter from yang model
Priority of initial writing default parameters into database:
- Database already contains default parameters
- User defines default parameters into config file
- Default values from yang schema file will be saved
Default parameters can be managed (read/update) using RESTCONF/Uniconfig shell with UniConfig Cloud Config.
Default parameters can also be defined in the application.properties.json
file located in the config directory.
# Netconf default parameters properties.
netconf-default-parameters.flags.enabled-notifications=true
netconf-default-parameters.flags.enabled-strict-parsing=true
netconf-default-parameters.flags.reconnect-on-changed-schema=false
netconf-default-parameters.flags.streaming-session=false
netconf-default-parameters.session-timers.between-attempts-timeout=2000
netconf-default-parameters.session-timers.confirm-commit-timeout=600
netconf-default-parameters.session-timers.initial-connection-timeout=20000
netconf-default-parameters.session-timers.keepalive-delay=120
netconf-default-parameters.session-timers.max-connection-attempts=1
netconf-default-parameters.session-timers.max-reconnection-attempts=0
netconf-default-parameters.session-timers.reconnection-attempts-multiplier=1.5
netconf-default-parameters.session-timers.request-transaction-timeout=60000
netconf-default-parameters.other-parameters.concurrent-rpc-limit=0
netconf-default-parameters.other-parameters.dry-run-journal-size=0
netconf-default-parameters.other-parameters.custom-connector-factory=default
netconf-default-parameters.other-parameters.edit-config-test-option=test-then-set
# GNMI default parameters
gnmi-default-parameters.session-timers.request-timeout=30
gnmi-default-parameters.session-timers.request-max-size=4194304
gnmi-default-parameters.flags.enabled-notifications=true
gnmi-default-parameters.other-parameters.dry-run-journal-size=0
# CLI default parameters
cli-default-parameters.max-connection-attempts=1
cli-default-parameters.max-reconnection-attempts=0
cli-default-parameters.max-connection-attempts-install=1
cli-default-parameters.dry-run-journal-size=0
cli-default-parameters.journal-level=command-only
cli-default-parameters.journal-size=0
cli-default-parameters.keepalive-delay=60
cli-default-parameters.keepalive-initial-delay=120
cli-default-parameters.keepalive-timeout=60
cli-default-parameters.command-timeout=60
cli-default-parameters.connection-establish-timeout=60
cli-default-parameters.connection-lazy-timeout=60
cli-default-parameters.parsing-engine=tree-parserRPC request - read CLI default parameters:
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/uniconfig-manager:read-properties' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"input": {
"property-keys": [
"cli-default-parameters.max-connection-attempts",
"cli-default-parameters.max-reconnection-attempts",
"cli-default-parameters.max-connection-attempts-install",
"cli-default-parameters.dry-run-journal-size",
"cli-default-parameters.journal-level",
"cli-default-parameters.journal-size",
"cli-default-parameters.keepalive-delay",
"cli-default-parameters.keepalive-initial-delay",
"cli-default-parameters.keepalive-timeout",
"cli-default-parameters.command-timeout",
"cli-default-parameters.connection-establish-timeout",
"cli-default-parameters.connection-lazy-timeout",
"cli-default-parameters.parsing-engine"
]
}
}'{
"output": {
"properties-map": [
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.max-connection-attempts-install",
"value": "1"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.max-connection-attempts",
"value": "1"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.max-reconnection-attempts",
"value": "0"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.dry-run-journal-size",
"value": "0"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.journal-level",
"value": "command-only"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.journal-size",
"value": "0"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.keepalive-delay",
"value": "60"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.keepalive-initial-delay",
"value": "120"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.keepalive-timeout",
"value": "60"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.command-timeout",
"value": "60"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.connection-establish-timeout",
"value": "60"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.connection-lazy-timeout",
"value": "60"
},
{
"name": "cli-default-parameters.parsing-engine",
"value": "tree-parser"
}
],
"read-properties-status": "There are 13 from 13 properties read successfully. Ignored keys: []"
}
}
#
Installing CLI device
List of basic connection parameters that are used for identification of remote device. All of these parameters are mandatory.
- node-id - Name of node that represents device in the topology.
- cli-topology:host - IP address or domain-name of target device that runs SSH or Telnet server.
- cli-topology:port - TCP port on which the SSH or Telnet server on remote device is listening to incoming connections. Standard SSH port is '22', standard Telnet port is '23'.
- cli-topology:transport-type - Application protocol used for communication with device - supported options are 'ssh' and 'telnet'.
- cli-topology:device-type - Device type that is used for selection of translation units that maps device configuration to OpenConfig models. Supported devices can be found
- cli-topology:device-version - Version of device. Use a specific version or * for a generic one. * enables only basic read and write management without the support of OpenConfig models. Here.
- cli-topology:username - Username for accessing of CLI management line.
- cli-topology:password - Password assigned to username.
- uniconfig-config:install-uniconfig-node-enabled - Whether node should be installed to UniConfig and unified layers. By default, this flag is set to 'true'.
#
Authentication parameters
List of authentication parameters used for identification of remote user utilized for configuration of the device. Username and password parameters are mandatory.
- cli-topology:username - Username for accessing of CLI management line.
- cli-topology:password - Password assigned to username.
List of parameters that can be used for adjusting of reconnection strategy. None of these parameters is mandatory - if they are not set, default values are set. There are two exclusive groups of parameters based on selected reconnection strategy - you can define only parameters from single group. By default, keepalive strategy is used.
#
Connection parameters
Following parameters adjust maintaining of CLI session state. None of these parameters are mandatory (default values will be used).
- cli-topology:max-connection-attempts - Maximum number of initial connection attempts
(default value: 1, non-positive value or null is interpreted as infinity). If there are unstable devices in the network it might be useful
to provide
max-connection-attemptshigher than the default value. It would try to connectntimes before throwing an ssh connection exception. - cli-topology:max-connection-attempts-install - Maximum number of initial connection attempts during install
process (default value: 1, non-positive value or null is interpreted as infinity). If there are unstable devices in the network it might be useful
to provide
max-connection-attempts-installhigher than the default value. It would try to connectntimes before throwing an ssh connection exception. - cli-topology:max-reconnection-attempts - Maximum number of reconnection attempts
(default value: 0, non-positive value or null is interpreted as infinity). It is used when open and established session dropped.
max-reconnection-attemptsis not that necessary to set. Uniconfig does not keep idle sessions open longer than it is necessary.
#
Storing failed installations
The following parameter allows the user to store the installation in case the device is in some way unreachable.
- uniconfig-config:store-failed-installation - If enabled, it will ensure that even if the device is unreachable, it will be stored in the node table in the database. If not set, the default value is false.
When the user sets the flag to true, an additional column called installation-status will be populated with a boolean flag (either SUCCESSFUL for a successful installation, or FAILED for a failed one). This lets the user know that there has been some problem and that the device was not installed correctly. The mount-point information of that node will be stored (unlike with the default value). With this info already stored, the user does not need to reinstall the device, as all the connection information is present in the UniConfig database. Syncing the device or calling a GET Request will try to reconnect to the device and if it is successful, the configuration data will be saved in the datastore and the request will then finish. The installation-status will then change to SUCCESSFUL. The installed device will then behave normally as if the installation was successful in the first place. If the device is still unreachable, the flag will stay FAILED.
This is useful when many devices are being installed in batches and the user doesn't know if they are up or not.
#
Installing without mount
The following parameter lets you store node metadata into the UniConfig database without mounting the node:
uniconfig-config:store-without-mount- When enabled, skip the mount procedure and store node metadata into the UniConfig database with installation statusFAILED. The default value isfalse.
This flag is primarily intended for scenarios where you want UniConfig to be aware of a specific node that is not yet up and reachable. Once the device is up, you can simply call the sync-from-network RPC to load the configuration. Additionally, this can reduce the lifetime of the install-node RPC, as it does not need to wait for connection failure.
#
Keepalive strategies
1. Keepalive reconnection strategy
- cli-topology:keepalive-delay - Delay between sending of keepalive messages over CLI session. The value should not be set higher than the execution of the longest operation. Default value: 60 seconds.
- cli-topology:keepalive-timeout - This parameter defines how much time the CLI layer should wait for a response to keepalive message before the session is closed. Default value: 60 seconds.
- cli-topology:keepalive-initial-delay - This parameter defines how much time CLI layer waits for establishment of new CLI session before the first reconnection attempt is launched. Default value: 120 seconds.
The keepalive parameters have two main functions:
- keep the idle session open
- timeout commands which would block the session forever
#
Example of using the connection and keepalive parameters together
For this example let us assume that we are dealing with a prod-like device, which would mean that some devices might have a large config. We would set these parameters:
max-connection-attempts=3
max-reconnection-attempts=3
keepalive-delay=120
keepalive-timeout=120Connection attempts would give us more flexibility if we work with unstable devices. It would try to ssh 3 times instead of 1 (default value). We should also keep in mind that the process of connecting to a device would take longer because of extra ssh attempts.
Keepalive commands can be set less than time of the installation, because keepalive commands can
fit in between of the installation process. An important thing to keep in mind is to set sum of
keepalive-delay and keepalive-timeout parameters higher than time of execution of the configuration
show command. Otherwise, it could time out during writing out of the configuration to the console.
For each type of device it is a different command (configuration show brief for Ciena devices,
show run for Cisco devices, etc.).
Assumption is that it should not take more than 240 seconds (sum of keepalive params) to show the
whole configuration. This can be appropriately adjusted to our circumstances.
2. Lazy reconnection strategy
- command-timeout - Maximal time (in seconds) for command execution. If a command cannot be executed on a device in this time, the execution is considered a failure. Default value: 60 seconds.
- connection-establish-timeout - Maximal time (in seconds) for connection establishment. If a connection attempt fails in this time, the attempt is considered a failure. Default value: 60 seconds.
- connection-lazy-timeout - Maximal time (in seconds) for connection to keep alive. If no activity was detected in the session and the timeout has been reached, connection will be stopped. Default value: 60 seconds.
#
Journaling parameters
The following parameters relate with tracing of executed commands. It is not required to set these parameters.
- cli-topology:journal-size - Size of the cli mount-point journal. Journal keeps track of executed commands and makes them available for users/apps for debugging purposes. Value 0 disables journaling (it is default value).
- cli-topology:dry-run-journal-size - Creates dry-run mount-point and defines number of commands in command history for dry-run mount-point. Value 0 disables dry-run functionality (it is default value).
- cli-topology:journal-level - Sets how much information should be stored in the journal. Option 'command-only' stores only the actual commands executed on device. Option 'extended' records additional information such as: transaction life-cycle, which handlers were invoked etc.
#
Parsing parameters
Parsing strategies are used for:
- Recognizing of structure in cached device configuration that is represented in textual format.
- Extraction of target sections from structured format of device configuration.
Parsing engine can be configured on creation of mountpoint by specification of parsing-engine leaf value. Currently, there are three supported CLI parsing strategies: tree-parser (default strategy), batch-parser and one-line-parser.
Both batch-parser and tree-parser depend on current implementation of 'CliFlavour' which defines device-specific CLI patterns. For example, if 'CliFlavour' doesn't correctly specify format of 'show configuration' command, then neither batch-parser or tree-parser is applied and commands are sent directly to device.
#
Tree-parser
- It is set as default parsing engine in case you choose to not use 'parsing-engine' parameter.
- Running-configuration is mapped into the tree structure before the first command lookup is executed from translation unit. Afterwards, this tree can be reused in the same transaction for faster lookup process (for example, one 'sync-from-network' task is executed in one transaction).
- Tree-parser is faster than batch-parser in most cases because device configuration must be traversed only once and searching for target section in parsed tree structure has only logarithmic time complexity. The longer the device configuration is, the better performance improvement is achieved using this parsing strategy.
- Both batch-parser and tree-parser should be capable to parse the same device configurations (in other words, tree-parser doesn't have any functional restrictions in comparison to batch-parser).
#
Batch-parser
- Running-configuration must be traversed from the beginning each time when new target section is extracted from the configuration (such lookup process is launched from CLI translation units).
- Internally, this parser uses regular expressions to recognize structure of configuration and find target section. From this reason, if configuration is long, this batch-parser becomes ineffective to extract sections that are placed near the end of device configuration.
- Batch-parser should be used only as fallback strategy in the case when tree-parser fails.
#
One-line-parser
- CLI parsing engine that stores configuration in the cache in the form of blocks and then uses grep function for parsing running-configuration
#
Cisco IOX XR Example request
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:install-node' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"input": {
"node-id": "iosxr",
"cli": {
"cli-topology:host": "192.168.1.214",
"cli-topology:port": "22",
"cli-topology:transport-type": "ssh",
"cli-topology:device-type": "ios xr",
"cli-topology:device-version": "5.3.4",
"cli-topology:username": "cisco",
"cli-topology:password": "cisco",
"cli-topology:journal-size": 150,
"cli-topology:dry-run-journal-size": 150,
"cli-topology:parsing-engine": "batch-parser",
"uniconfig-config:install-uniconfig-node-enabled": false
}
}
}'
#
Junos Example request
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:install-node' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"input": {
"node-id": "junos",
"cli": {
"cli-topology:host": "192.168.1.25",
"cli-topology:port": "22",
"cli-topology:transport-type": "ssh",
"cli-topology:device-type": "junos",
"cli-topology:device-version": "17.3",
"cli-topology:username": "root",
"cli-topology:password": "Agiebiz2",
"cli-topology:journal-size": 150,
"uniconfig-config:install-uniconfig-node-enabled": false
}
}
}'
#
Uninstalling CLI device
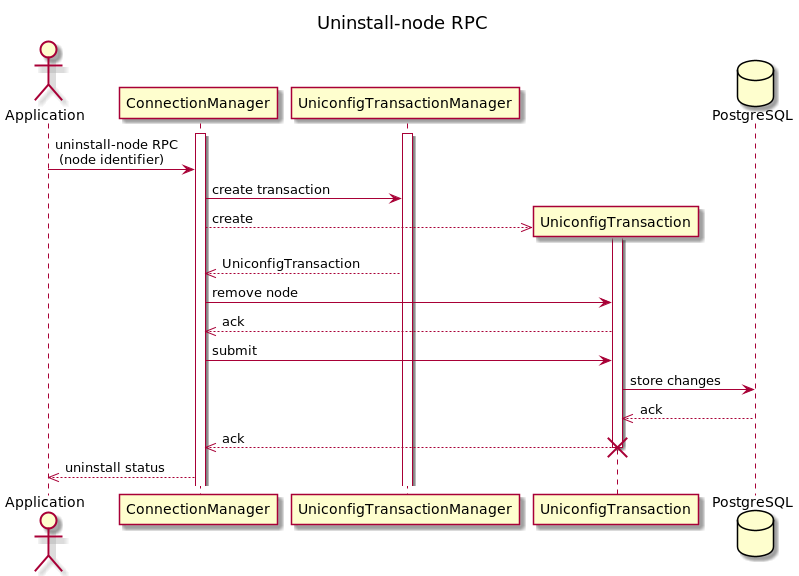
#
Example request
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:uninstall-node' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"input": {
"node-id": "junos",
"connection-type": "cli"
}
}'
#
Installing Netconf device
#
Identification of remote device
List of basic connection parameters that are used for identification of remote device. Only tcp-only parameter must not be specified in input of the request.
- node-id - Name of node that represents device / mount-point in the topology.
- netconf-node-topology:host - IP address or domain-name of target device that runs NETCONF server.
- netconf-node-topology:port - TCP port on which NETCONF server is listening to incoming connections.
- netconf-node-topology:tcp-only - If it is set to 'true', NETCONF session is created directly on top of TCP connection. Otherwise, 'SSH' is used as carriage protocol. By default, this parameter is set to 'false'.
#
Authentication parameters
Parameters used for configuration of the basic authentication method against NETCONF server. These parameters must be specified in the input request.
- network-topology:username - Name of the user that has permission to access device using NETCONF management line.
- network-topology:password - Password to the user in non-encrypted format.
There are also other authentication parameters if different authentication method is used - for example, key-based authentication requires specification of key-id. All available authentication parameters can be found in netconf-node-topology.yang under netconf-node-credentials grouping.
#
Session timers
The following parameters adjust timers that are related with maintaining of NETCONF session state. None of these parameters are mandatory (default values will be used).
- netconf-node-topology:initial-connection-timeout - Specifies timeout in seconds after which initial connection to the NETCONF server must be established (default value: 20 s).
- netconf-node-topology:request-transaction-timeout - Timeout for blocking RPC operations within transactions (default value: 60 s).
- netconf-node-topology:max-connection-attempts - Maximum number of connection attempts (default value: 1, non-positive value or null is interpreted as infinity).
- netconf-node-topology:max-reconnection-attempts - Maximum number of reconnection attempts. It is used when ongoing session dropped (default value: 0, non-positive value or null is interpreted as infinity).
- netconf-node-topology:between-attempts-timeout - Initial timeout between reconnection attempts (default value: 2 s).
- netconf-node-topology:reconnenction-attempts-multiplier - Multiplier between subsequent delays of reconnection attempts (default value: 1.5).
- netconf-node-topology:keepalive-delay - Delay between sending of keepalive RPC messages (default value: 120 sec).
- netconf-node-topology:confirm-commit-timeout - The timeout for confirming the configuration by "confirming-commit" that was configured by "confirmed-commit". Configuration will be automatically reverted by device if the "confirming-commit" is not issued within the timeout period. This parameter has effect only on NETCONF nodes. (default value: 600 sec).
#
Capabilities
Parameters related to capabilities are often used when NETCONF device doesn't provide list of YANGs. Both parameters are optional.
- netconf-node-topology:yang-module-capabilities - Set a list of capabilities to override capabilities provided in device's hello message. It can be used for devices that do not report any yang modules in their hello message.
- netconf-node-topology:non-module-capabilities - Set a list of non-module based capabilities to override or merge non-module capabilities provided in device's hello message. It can be used for devices that do not report or incorrectly report non-module-based capabilities in their hello message.
Instead of defining netconf-node-topology:yang-module-capabilities, we can just define folder with yang schemas netconf-node-topology:schema-cache-directory: folder-name. For more information about using the netconf-node-topology:schema-cache-directory parameter, see RST Other parameters.
#
UniConfig-native
Parameters related to installation of NETCONF or CLI nodes with uniconfig-native support.
- uniconfig-config:uniconfig-native-enabled - Whether uniconfig-native should be used for installation of NETCONF or CLI node. By default, this flag is set to 'false'.
- uniconfig-config:install-uniconfig-node-enabled - Whether node should be installed to UniConfig and unified layers. By default, this flag is set to 'true'.
- uniconfig-config:sequence-read-active - Force sequential data reading when mounting a device. If set to 'true', sync-from-network is done in parallel. The default value is 'false'.
- uniconfig-config:whitelist - List of root YANG entities that should be read.
- uniconfig-config:blacklist - List of root YANG entities that should not be read from NETCONF device due to incompatibility with uniconfig-native or other malfunctions in YANG schemas. This parameter has effect only on NETCONF nodes.
- uniconfig-config:validation-enabled - Whether validation RPC should be used before submitting configuration of node. By default, this flag is set to 'true'. This parameter has effect only on NETCONF nodes.
- uniconfig-config:confirmed-commit-enabled - Whether confirmed-commit RPC should be used before submitting configuration of node. By default, this flag is set to 'true'. This parameter has effect only on NETCONF nodes.
- uniconfig-config:store-failed-installation - Whether the installation
should be stored in the database if it fails (e.g. is unreachable).
The node will be 'installed' even though it failed and the user has 2 options:
- uninstall the device and reinstall it.
- call sync-from-network to sync the data from the device.
#
Flags
Non-mandatory flag parameters that can be added to mount-request.
- netconf-node-topology:enabled-strict-parsing - Default value of enabled-strict-parsing parameter is set to 'true'. This may inflicts in throwing exception during parsing of received NETCONF messages in case of unknown elements. If this parameter is set to 'false', then parser should ignore unknown elements and not throw exception during parsing.
- netconf-node-topology:enabled-notifications - Default value of enabled-notifications is set to 'true'. If it is set to 'true' and NETCONF device supports notifications, NETCONF mountpoint will expose NETCONF notification and subscription services.
- netconf-node-topology:reconnect-on-changed-schema - Default value of reconnect-on-changed-schema is set to 'false'. If it is set to 'true', NETCONF notifications are supported by device, and NETCONF notifications are enabled ('enabled-notifications' flag), the connector would auto disconnect/reconnect when schemas are changed in the remote device. The connector subscribes (right after connect) to base netconf notifications and listens for netconf-capability-change notification
- netconf-node-topology:streaming-session - Default value of streaming-session parameter is set to 'false'. NETCONF session is created and optimized for receiving of NETCONF notifications from remote server.
#
Other parameters
Other non-mandatory parameters that can be added to mount-request.
netconf-node-topology:schema-cache-directory - This parameter can be used for two cases:
- Explicitly set name of NETCONF cache directory. If it is not set, the name of the schema cache directory is derived from device capabilities during mounting process.
- Direct usage of the 'custom' NETCONF cache directory stored in the UniConfig 'cache' directory by name. This 'custom' directory must exist, must not be empty and also can not use the 'netconf-node-topology:yang-module-capabilities' parameter, because capability names will be generated from yang schemas stored in the 'custom' directory.
netconf-node-topology:dry-run-journal-size - Creates dry-run mount-point and defines number of NETCONF RPCs in history for dry-run mount-point. Value 0 disables dry-run functionality (it is default value).
netconf-node-topology:custom-connector-factory - Specification of the custom NETCONF connector factory. For example, if device doesn't support candidate data-store, this parameter should be set to 'netconf-customization-alu-ignore-candidate' string (default value is "default").
netconf-node-topology:edit-config-test-option - Specification of the test-option parameter in the netconf edit-config message. Possible values are 'set', 'test-then-set' or 'test-only'. If the edit-config-test-option is not explicitly specified in the mount request, then the default value will be used ('test-then-set'). See RFC-6241 for more information about this feature.
netconf-node-topology:concurrent-rpc-limit - Defines maximum number of concurrent RPCs, where 0 indicates no limit (it is default value).
There are additional install parameters in our OpenAPI, they can all be found here.
#
Example netconf request
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:install-node' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"input":{
"node-id":"xr1",
"netconf":{
"netconf-node-topology:host":"10.0.0.1",
"netconf-node-topology:port":830,
"netconf-node-topology:tcp-only":false,
"netconf-node-topology:username":"USERNAME",
"netconf-node-topology:password":"PASSWORD",
"netconf-node-topology:session-timers" : {
"netconf-node-topology:keepalive-delay": 5
},
"netconf-node-topology:other-parameters" : {
"netconf-node-topology:dry-run-journal-size": 180
},
"uniconfig-config:uniconfig-native-enabled":true,
"uniconfig-config:blacklist":{
"uniconfig-config:path":[
"openconfig-interfaces:interfaces",
"ietf-interfaces:interfaces",
"openconfig-vlan:vlans",
"openconfig-routing-policy:routing-policy",
"openconfig-lldp:lldp",
"Cisco-IOS-XR-l2vpn-cfg:l2vpn",
"Cisco-IOS-XR-group-cfg:groups",
"openconfig-acl:acl",
"openconfig-network-instance:network-instances"
]
}
}
}
}'
#
Uninstalling Netconf device
#
Example request
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:uninstall-node' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"input": {
"node-id": "xr1",
"connection-type": "netconf"
}
}'
#
Installing gNMI device
#
Identifying remote device
Basic connection parameters used to identify a remote device:
node-id- Name of the node that represents the device/mountpoint in the topology.gnmi-topology:host- IP address or domain name of the target device running the gNMI server.gnmi-topology:port- TCP port where the gNMI server is listening to incoming connections.gnmi-topology:device-type- Specific device type, which enables some device-specific behavior. By default, this parameter is not specified.gnmi-topology:connection-type- If specified, an insecure connection is created. The insecure connection is available only for DEBUG reasons. To establish a gRPC connection without TLS, choose the insecure connection typePLAINTEXT. The connection typePLAINTEXTindicates that the target should skip the signature verification steps if a secure connection is used.gnmi-topology:keystore-id- If specified, a secure connection is created. Also requireskeystore-id(identifier of the keystore), which is defined in thegnmi-certificate-storagemodel.
Only one of the parameters keystore-id and connection-type can be specified.
#
Authentication parameters
Parameters to configure the basic authentication method against a gNMI server. These parameters must be specified in the input request inside the gnmi-topology:credentials container:
gnmi-topology:username- Username with permission to access the device using gNMI.gnmi-topology:password- Password for username.
#
Session timers
The following parameters adjust timers related to maintaining gNMI session state. None of these parameters are mandatory (default values are used if not specified):
gnmi-topology:request-timeout- Timeout (in seconds) for each gNMI request. The request times out if not completed in time. The default value is 30.
#
Flags
Non-mandatory flag parameters that can be added to a mount request:
gnmi-topology:enabled-notifications- If set totrueand the gNMI device supports notifications, the gNMI mountpoint will expose GNMI notification and subscription services. The default value istrue.
#
Other parameters
Other non-mandatory parameters that can be added to a mount request:
gnmi-topology:dry-run-journal-size- Size of the dry-run gNMI mountpoint journal. The dry-run journal captures gNMI operations that would be executed when reading/writing a configuration. However, the operations are not actually sent to the device. The default value is 0.
#
Extension parameters
Other extended non-mandatory parameters that can be added to a mount-request inside of the extensions-parameters container.
#
gNMI parameters
gnmi-topology:use-model-name-prefix- Some devices require a module prefix in the first element name of the gNMI request path (for example, interfaces -> openconfig-interfaces:interfaces). The default value isfalse.
#
UniConfig-native
Parameters related to installing gNMI nodes with uniconfig-native support:
uniconfig-config:uniconfig-native-enabled- Whether or not uniconfig-native should be used for installing of NETCONF, CLI or gNMI nodes. The default value isfalse.uniconfig-config:sequence-read-active- Forces reading of data sequentially when mounting a device. If set totrue, sync-from-network is done in parallel. The default value isfalse.uniconfig-config:whitelist- List of root YANG entities that should be read.uniconfig-config:store-failed-installation- Whether or not the installation is stored in the database if it fails (e.g., unreachable). The node is "installed" even though it fails, and the user has two options:- Uninstall the device and reinstall it.
- Call
sync-from-networkto sync the data from the device.
An important install parameter is gnmi-topology:schema-cache-directory: <folder-name>. It specifies a folder name
in the cache directory with the YANG schemas needed to install a device. If this parameter is not specified,
user can create default-capability.json file inside of mentioned cache directory and UniConfig will dynamically
resolve correct cache directory for given node. This json file must have all capabilities that device supports.
Format of default-capability.json:
[
{
"name": "nokia-conf",
"organization": "Nokia",
"version": "22.10.R7"
},
{
"name": "nokia-state",
"organization": "Nokia"
},
{
"name": "nokia-li-state"
}
]
#
Update paths
This is a non-mandatory parameter that specifies a list of paths for which UniConfig will process intended changes as a gNMI SET message - Update operation. Paths are specified in regexp format.
More information about update paths feature: https://docs.frinx.io/frinx-uniconfig/user-guide/network-management-protocols/uniconfig_gnmi/#update-paths.
#
Replace paths
This is a non-mandatory parameter that specifies a list of paths for which UniConfig will process intended changes as a gNMI SET message - Replace operation.
A specific replace diff implementation in UniConfig checks and merges all changes according to the specified replace-paths, and ensures that the gNMI SET message has the same path as the one specified in replace-paths in the install request.
Paths are specified in common RESTful URL format, but list entries can be compiled as a regexp pattern if specified with the $ sign after the = sign.
More information about the replace paths feature: https://docs.frinx.io/frinx-uniconfig/user-guide/network-management-protocols/uniconfig_gnmi/#replace-paths.
#
Remove module name paths
This is a non-mandatory parameter that specifies a list of paths for which UniConfig removes the module name of specified list entry keys. (For example, protocol=openconfig-policy-types:BGP,bgp, remove-module-name-path = network-instances/network-instance=$.*/protocols/protocol).
The path format is the same as for replace-paths.
#
All type paths
This is a non-mandatory parameter that specifies a list of paths for which UniConfig provides a GET request with the ALL data type.
The path format is the same as for replace-paths.
This feature only applies to the SONiC device type.
#
Dependency paths
This is a non-mandatory parameter that specifies list of paths for which UniConfig will check and order the intended changes.
The format of dependency paths:
before- path without keys that is ordered before the path specified inafter.after- path without keys that is ordered after the path specified inbefore.
More information about dependency paths: https://docs.frinx.io/frinx-uniconfig/user-guide/network-management-protocols/uniconfig_gnmi/#dependency-paths.
#
Example request
curl --location 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:install-node' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"input": {
"node-id": "sonic",
"gnmi": {
"schema-cache-directory": "gnmi-topology",
"update-paths": [
"openconfig-interfaces:interfaces\/interface=.*[Ee]thernet?[0-9]+\/.*",
"[^\/]+",
"sonic-vlan:sonic-vlan.*"
],
"replace-paths": [
"openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface=$.*[Ee]thernet?[0-9]+/openconfig-if-ethernet:ethernet/openconfig-vlan:switched-vlan/config/trunk-vlans",
"openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface=$.*[Pp]ortChannel?[0-9]+/openconfig-if-aggregate:aggregation/openconfig-vlan:switched-vlan/config/trunk-vlans",
"openconfig-relay-agent:relay-agent/dhcp/interfaces/interface=$[Vv]lan[0-9]+/config",
"openconfig-relay-agent:relay-agent/dhcpv6/interfaces/interface=$[Vv]lan[0-9]+/config",
"openconfig-platform:components/component=$.*/openconfig-platform:port/openconfig-platform-port:breakout-mode"
],
"remove-module-names-paths": [
"network-instances/network-instance=default/protocols/protocol"
],
"all-type-paths": [
"openconfig-lldp:lldp",
"openconfig-port-group:port-groups"
],
"dependency-paths": [
{
"before": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance",
"after": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance/interfaces/interface"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance/interfaces/interface",
"after": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance/openconfig-vxlan:vxlan-vni-instances/vni-instance"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance/interfaces/interface",
"after": "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface/openconfig-vlan:routed-vlan/openconfig-if-ip:ipv4/openconfig-interfaces-ext:sag-ipv4/config"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance/interfaces/interface",
"after": "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface/openconfig-vlan:routed-vlan/openconfig-if-ip:ipv6/openconfig-interfaces-ext:sag-ipv6/config"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance/openconfig-vxlan:vxlan-vni-instances/vni-instance",
"after": "openconfig-relay-agent:relay-agent/dhcp/interfaces/interface"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance/openconfig-vxlan:vxlan-vni-instances/vni-instance",
"after": "openconfig-relay-agent:relay-agent/dhcpv6/interfaces/interface"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface/openconfig-vlan:routed-vlan/openconfig-if-ip:ipv4/openconfig-interfaces-ext:sag-ipv4/config",
"after": "openconfig-relay-agent:relay-agent/dhcp/interfaces/interface"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface/openconfig-vlan:routed-vlan/openconfig-if-ip:ipv6/openconfig-interfaces-ext:sag-ipv6/config",
"after": "openconfig-relay-agent:relay-agent/dhcpv6/interfaces/interface"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface",
"after": "openconfig-mclag:mclag/interfaces/interface"
},
{
"before": "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface",
"after": "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface/openconfig-if-ethernet:ethernet/config/aggregate-id"
},
{
"before" : "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface",
"after": "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance/interfaces/interface"
},
{
"before" : "openconfig-network-instance:network-instances/network-instance",
"after": "openconfig-interfaces:interfaces/interface/subinterfaces"
}
],
"uniconfig-config:whitelist": {
"path": [
"openconfig-interfaces:interfaces",
"openconfig-network-instance:network-instances",
"openconfig-relay-agent:relay-agent",
"openconfig-port-group:port-groups",
"openconfig-mclag:mclag",
"openconfig-lldp:lldp",
"sonic-vlan:sonic-vlan",
"openconfig-platform:components",
"openconfig-system:system",
"openconfig-neighbor:neighbor-globals",
"sonic-mclag:sonic-mclag"
]
},
"uniconfig-config:uniconfig-native-enabled": true,
"uniconfig-config:sequence-read-active": true,
"connection-parameters": {
"host": "<ip>",
"port": "8080",
"device-type" : "sonic",
"connection-type": "INSECURE",
"credentials": {
"username": "<username>",
"password": "<password>"
}
},
"session-timers": {
"request-timeout" : 180
},
"other-parameters" : {
"dry-run-journal-size" : 240
},
"extensions-parameters": {
"gnmi-parameters": {
"use-model-name-prefix": true
},
"force-cached-capabilities": [
null
]
}
}
}
}'
#
Uninstalling gNMI device
#
Example request
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:uninstall-node' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"input": {
"node-id": "r1",
"connection-type": "gnmi"
}
}'
#
Installing SNMP agent
#
Identification of remote agent
List of basic connection parameters that are used for identification of remote agent.
- node-id - Name of node that represents device / mount-point in the topology.
- snmp-topology:host - IP address or domain-name of target device where SNMP agent is running.
- snmp-topology:port - SNMP port on which SNMP agent is listening to incoming connections.
#
SNMP parameters
- snmp-topology:transport-type - UniConfig currently supports UDP for SNMP communication, with plans to add TCP support in the future.
- snmp-topology:snmp-version - UniConfig currently supports V1 and V2c version of the SNMP, with plans to add V3 support in the future.
- snmp-topology:connection-retries - Sets the number of retries to be performed before a request is timed out. Default value is 0.
- snmp-topology:request-timeout - Timeout in milliseconds before a confirmed request is resent or timed out. Default value is 3000.
- snmp-topology:get-bulk-size - The maximum number of values that can be returned in a single response to the get-bulk operation. Default value is 50.
#
Authentication parameters
- snmp-topology:community-string - UniConfig currently supports only security string as authentication method that is used with V1 and V2c.
#
Others
- snmp-topology:mib-repository - Name of the MIB repository that contains MIB files.
#
Example request
curl --location 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:install-node' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"input": {
"node-id": "agent1",
"snmp": {
"snmp-topology:host": "192.168.1.225",
"snmp-topology:port": 161,
"snmp-topology:transport-type": "udp",
"snmp-topology:snmp-version": "v2c",
"snmp-topology:community-string": "public",
"snmp-topology:connection-retries": 1,
"snmp-topology:request-timeout": 5000,
"snmp-topology:get-bulk-size": "900",
"snmp-topology:mib-repository": "repo1"
}
}
}'
#
Uninstalling SNMP agent
#
Example request
curl --location 'http://localhost:8181/rests/operations/connection-manager:uninstall-node' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"input": {
"node-id": "agent1",
"connection-type": "snmp"
}
}'