#
Create and Modify Workflows and Workers
#
Prepare Your Work Environment
After you have installed and started the FRINX Machine (see "https://github.com/FRINXio/FRINX-machine") you will want to modify existing workflows or add new workflows and workers to meet your needs. We will be referring to the machine that is running the FRINX Machine containers as host. Typically that host is a VM running on your laptop, in your private cloud or in a public/virtual private cloud. Here is how to get started.
#
Creating a worker
Now that we have our environment prepared, we can move on to the first step of creating a workflow. First we will create a worker that defines the tasks utilized in our workflow. The goal is to have the task in our workflow receive two input parameters (id_1 and id_2). The purpose of our task is to add the two input variables and return the result. The execution logic of our task will be implemented in a small python function called worker.
For a full documentation of tasks, workflows and the capabilities of Netflix Conductor, please go to https://netflix.github.io/conductor/
Create a worker in a correct repository (name of the worker is up to you):
~/FRINX-machine/fm-workflows/demo-workflows/workers$ touch add_integers_worker.pyThis is what we put in the file in our case:
from __future__ import print_function
def execute_add_two_integers(task):
addend_one = task['inputData']['id_1']
addend_two = task['inputData']['id_2']
result = int(addend_one) + int(addend_two)
return {'status': 'COMPLETED', 'output': {'result': result}, 'logs': []}
def start(cc):
print('Starting add_two_integers worker')
cc.register('add_two_integers', {
"name": "add_two_integers",
"retryCount": 0,
"timeoutSeconds": 30,
"inputKeys": [
"id_1",
"id_2"
],
"timeoutPolicy": "TIME_OUT_WF",
"retryLogic": "FIXED",
"retryDelaySeconds": 0,
"responseTimeoutSeconds": 30
}
)
cc.start('add_two_integers', execute_add_two_integers, False)Core of the worker is a task that contains simple method which does addition with two inputs which user provides in GUI as you will see later. Workers can have multiple tasks within itself, in our case one is enough as an example.
After this, you must register your worker in the main python file "main.py" in the same directory where you just created your worker. All workers you want to use in Frinx Machine must be included in this file. File might look similar to this:
import time
import worker_wrapper
from frinx_rest import conductor_url_base
import inventory_worker
import lldp_worker
import platform_worker
import vll_worker
import unified_worker
import vll_service_worker
import vpls_worker
import vpls_service_worker
import bi_service_worker
import common_worker
import psql_worker
from import_workflows import import_workflows
import cli_worker
import netconf_worker
import uniconfig_worker
import http_worker
from importDevices import import_devices
import os
import add_integers_worker
workflows_folder_path = '../workflows'
healtchchek_file_path = '../healthcheck'
def main():
if os.path.exists(healtchchek_file_path):
os.remove(healtchchek_file_path)
print('Starting FRINX workers')
cc = worker_wrapper.ExceptionHandlingConductorWrapper(conductor_url_base, 1, 1)
register_workers(cc)
import_workflows(workflows_folder_path)
import_devices("../devices/cli_device_data.csv", "../devices/cli_device_import.json")
import_devices("../devices/netconf_device_data.csv", "../devices/netconf_device_import.json")
with open(healtchchek_file_path, 'w'): pass
# block
while 1:
time.sleep(1000)
def register_workers(cc):
platform_worker.start(cc)
lldp_worker.start(cc)
inventory_worker.start(cc)
unified_worker.start(cc)
psql_worker.start(cc)
add_integers_worker.start(cc)
# vll_worker.start(cc)
# vll_service_worker.start(cc)
# vpls_worker.start(cc)
# vpls_service_worker.start(cc)
# bi_service_worker.start(cc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()Notice lines 22 and 53, you must import both the worker file and include it in "register_workers(cc)" method.
That is all in terms of worker creation. There is however few more things to do in your environment. After doing all the above, we will want to build our Frinx Machine based on our local changes. For that we must edit the file "swarm-fm-workflow.yml"
~/FRINX-machine/fm-workflows/composefiles$ ls
swarm-fm-workflows.ymlFind block "demo-workflows" in this file. Change the image to use a image called "local" (2):
demo-workflows:
image: frinx/demo-workflows:local
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-file: "3"
max-size: "10m"
environment:
- UNICONFIG_URL_BASE=https://${CONSTRAINT_HOSTNAME}_uniconfig:8181/rests
healthcheck:
test: cat /home/app/healthcheck
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
start_period: 10s
deploy:
# placement:
# constraints:
# - node.hostname == ${CONSTRAINT_HOSTNAME}
mode: replicated
replicas: 1Now we can build our fm-workflows image with the added task. Use:
~/FRINX-machine/fm-workflows$
docker build --no-cache -f demo-workflows/Dockerfile -t frinx/demo-workflows:local ./demo-workflows/ While it is not necessary to use "--no-cache" flag, we recommend it to make sure you rebuild the image with newly edited code and not the one stored in cache memory.
Now just start fm-workflows and you're good to go:
~/FRINX-machine/fm-workflows$
./startup.shIf you did everything correctly, you will now see your new task in Frinx Machine. Go to Workflow Manager -> Tasks -> Search:
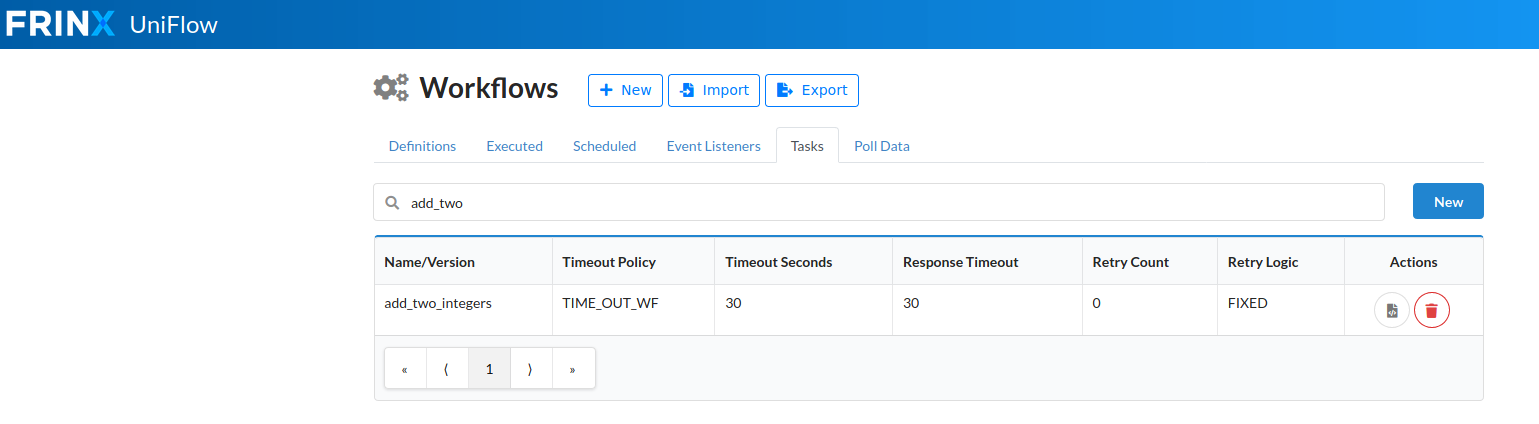
Now you can create workflow that uses this task. Workflow Manager -> "+ New":
#
After being prompted for inputs, you should see that addition ran successfully:
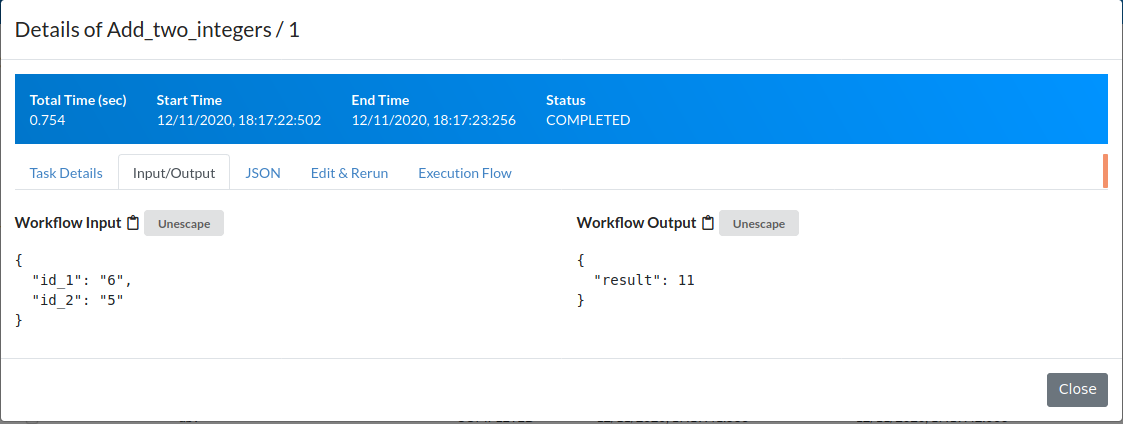
{
"taskType": "add_two_integers",
"status": "COMPLETED",
"inputData": {
"id_1": "6",
"id_2": "5"
},
"referenceTaskName": "add_two_integers_ref_XCFR",
"retryCount": 0,
"seq": 1,
"pollCount": 1,
"taskDefName": "add_two_integers",
"scheduledTime": 1607707042557,
"startTime": 1607707043195,
"endTime": 1607707043237,
"updateTime": 1607707043196,
"startDelayInSeconds": 0,
"retried": false,
"executed": true,
"callbackFromWorker": true,
"responseTimeoutSeconds": 30,
"workflowInstanceId": "1fcf782c-1cd6-4219-a6eb-e9d218de8b80",
"workflowType": "Add_two_integers",
"taskId": "9b88a65e-9869-420c-bd05-d42963948a39",
"callbackAfterSeconds": 0,
"workerId": "b5592d30c747",
"outputData": {
"result": 11
},
"workflowTask": {
"name": "add_two_integers",
"taskReferenceName": "add_two_integers_ref_XCFR",
"inputParameters": {
"id_1": "${workflow.input.id_1}",
"id_2": "${workflow.input.id_2}"
},
"type": "SIMPLE",
"decisionCases": {},
"defaultCase": [],
"forkTasks": [],
"startDelay": 0,
"joinOn": [],
"optional": false,
"taskDefinition": {
"createTime": 1607703392256,
"createdBy": "",
"name": "add_two_integers",
"retryCount": 0,
"timeoutSeconds": 30,
"inputKeys": [
"id_1",
"id_2"
],
"outputKeys": [],
"timeoutPolicy": "TIME_OUT_WF",
"retryLogic": "FIXED",
"retryDelaySeconds": 0,
"responseTimeoutSeconds": 30,
"inputTemplate": {},
"rateLimitPerFrequency": 0,
"rateLimitFrequencyInSeconds": 1
},
"defaultExclusiveJoinTask": [],
"asyncComplete": false,
"loopOver": []
},
"rateLimitPerFrequency": 0,
"rateLimitFrequencyInSeconds": 1,
"workflowPriority": 0,
"iteration": 0,
"taskDefinition": {
"present": true
},
"loopOverTask": false,
"taskStatus": "COMPLETED",
"queueWaitTime": 638,
"logs": []
}